Arrhythmias in normal infants & children
- Sinus arrhythmia
- Transient 2o AV block
- Atrial / ventricular extrasystoles
- Short runs of VT
- Sinus bradycardia, sinus pauses
Major arrhythmias in infants & children
- Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT)
- Ventricular tachycardia (VT)
- Complete Heart Block (CHB)
- Arrhythmias in special settings
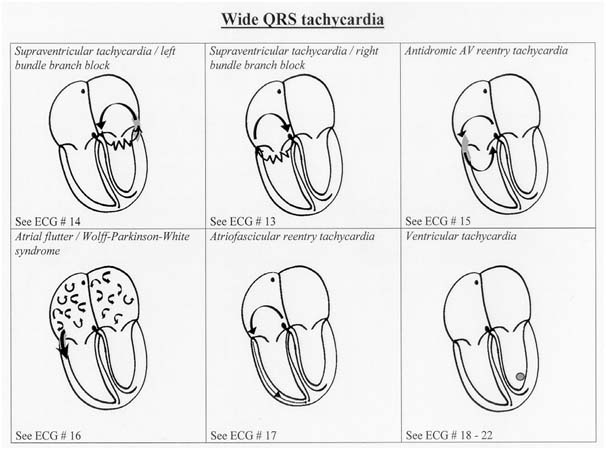
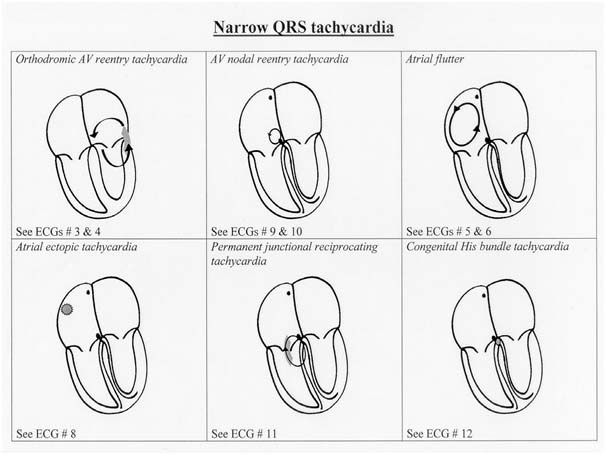
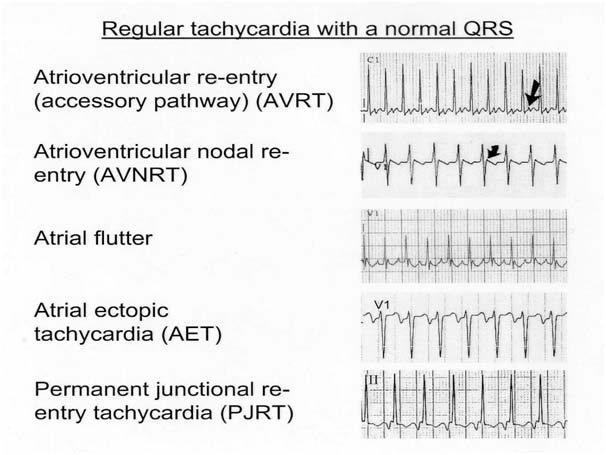
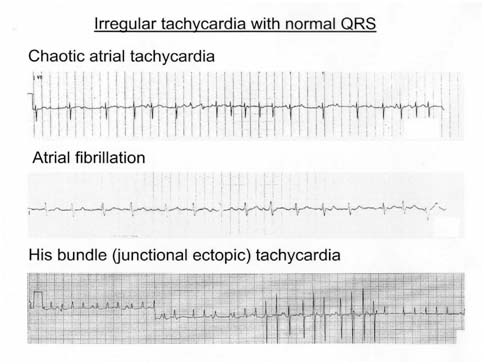
SVT
- Commonest serious arrhythmia in children
- Mechanism - reentry commonest
- Accessory pathway (80%)
- AV Nodal re-entry (20%)
SVT Presentation
Neonates/infants
- Unexplained "sickness"
- Recognition by parents
- CHF / Shock
Children
- Palpitation
- Recognition by parents
SVT Treatment
- Patient's factors : - age
- normal or abnormal heart
- frequency and duration of T.
- symptoms, hemodynamics
- other drugs
- Doctor's factors: - personal drug preference
- culture
- Vagal maneuvers
- Anti-arrhythmic drugs ( i.v. or oral)
- Electrical termination
- DC cardioversion
- Endocardial pacing
- Trans-esophageal pacing
- Adenosine 100-500 microgram/kg BOLUS
- Verapamil-contraindicated < 4 yrs.Useful in older children.0.1mg/kg iv.
- Propranolol 0.1mg/kg iv
- Digitalisation
- Propafenone , Flecainide 0.5-2 mg/kg iv
- Amiodarone 5mg/kg in 30 min,0.5-1mg/hr
- Cardioversion 05-1 J/kg
VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA
- Rare ,but does occur in children.
- Long QT syndrome,post cardiac surgery,idiopathic
- Rapid deterioration may occur
- IV Lignocaine o.5 mg/kg bolus, Amiodarone
- Cardioversion